Product name:Papain
Product description:Papain, also known as papaya proteinase I, is a cysteine protease enzyme present in papaya and mountain papaya .
Papain family:Papain belongs to a family of related proteins with a wide variety of activities, including endopeptidases, aminopeptidases, dipeptidyl peptidases and enzymes with both exo- and endo-peptidase activity. Members of the papain family are widespread, found in baculovirus,eubacteria, yeast, and practically all protozoa, plants and mammals.The proteins are typically lysosomal or secreted, and proteolytic cleavage of the propeptide is required for enzyme activation, although bleomycin hydrolase is cytosolic in fungi and mammals.Papain-like cysteine proteinases are essentially synthesised as inactive proenzymes (zymogens) with N-terminal propeptide regions. The activation process of these enzymes includes the removal of propeptide regions, which serve a variety of functions in vivo and in vitro. The pro-region is required for the proper folding of the newly synthesised enzyme, the inactivation of the peptidase domain and stabilisation of the enzyme against denaturing at neutral to alkaline pH conditions. Amino acid residues within the pro-region mediate their membrane association, and play a role in the transport of the proenzyme to lysosomes. Among the most notable features of propeptides is their ability to inhibit the activity of their cognate enzymes and that certain propeptides exhibit high selectivity for inhibition of the peptidases from which they originate.
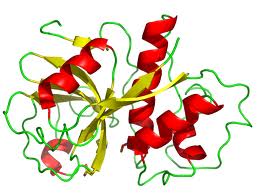
Structure:The papain precursor protein contains 345 amino acid residues,and consists of a signal sequence , a propeptide and the mature peptide . The amino acid numbers are based on the mature peptide. The protein is stabilised by three disulfide bridges. Its three-dimensional structure consists of two distinct structural domains with a cleft between them. This cleft contains the active site, which contains a catalytic diad that has been likened to the catalytic triad of chymotrypsin. The catalytic diad is made up of the amino acids - cysteine-25 (from which it gets its classification) and histidine-159. Aspartate-158 was thought to play a role analogous to the role of aspartate in the serine protease catalytic triad, but that has since then been disproved.[6] Nonetheless, it does appear to play a role.
Function:The mechanism by which it breaks peptide bonds involves deprotonation of Cys-25 by His-159. Asparagine-175 helps to orient the imidazole ring of His-159 to allow this deprotonation to take place. Cys-25 then performs a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of a peptide backbone. This frees the amino terminal of the peptide, and forms a covalent acyl-enzyme intermediate. The enzyme is then deacylated by a water molecule, and releases the carboxy terminal portion of the peptide. In immunology, papain is known to cleave the Fc (crystallisable) portion of immunoglobulins (antibodies) from the Fab (antigen-binding) portion.
Papain is a relatively heat resistant enzyme, with a temperature optimal range of 60-70°C.[7]
Papain prefers to cleave at: (hydrophobic)-(Arg or Lys)- cleaves here -(not Val). Hydrophobic is Ala, Val, Leu, Ile, Phe, Trp, or Tyr.
Uses:Its utility is in breaking down tough meat fibres and has been used for thousands of years in its native South America. It is sold as a component of powdered meat tenderiser available in most supermarkets. Papain, in the form of a meat tenderiser such as Adolph's, made into a paste with water, is also a home remedy treatment for jellyfish, bee, and yellow jacket (wasps) stings; mosquito bites; and possibly stingray wounds, breaking down the protein toxins in the venom.Papain can be used to dissociate cells in the first step of cell culture preparations. A ten-minute treatment of small tissue pieces (less than 1 mm cubed) will allow papain to begin breaking down the extracellular matrix molecules holding the cells together. After ten minutes, the tissue should be treated with a protease inhibitor solution to stop the protease action (if left untreated, papain's activity will lead to complete lysis of the cells). The tissue must then be triturated (passed quickly up and down through a Pasteur pipette) to break up the pieces of tissue into a single cell suspension.
It is also used as an ingredient in various enzymatic debriding preparations, notably Accuzyme. These are used in the care of some chronic wounds to clean up dead tissue.
Papain can also be found as an ingredient in some toothpastes or mints as teeth-whitener. Its whitening effect in toothpastes and mints is minimal, however, because the papain is present in low concentrations, and is quickly diluted by saliva. It would take several months of using the whitening product to have noticeably whiter teeth.
It is the main ingredient of Papacarie, a gel used for chemomechanical dental caries removal. Besides the advantage of avoiding the use of rotary cutting tools, it does not interfere in the bond strength of restorative materials to dentin.
Papain has been known to interfere with urine drug test for cannabinoids.It is found in some drug detox products.

